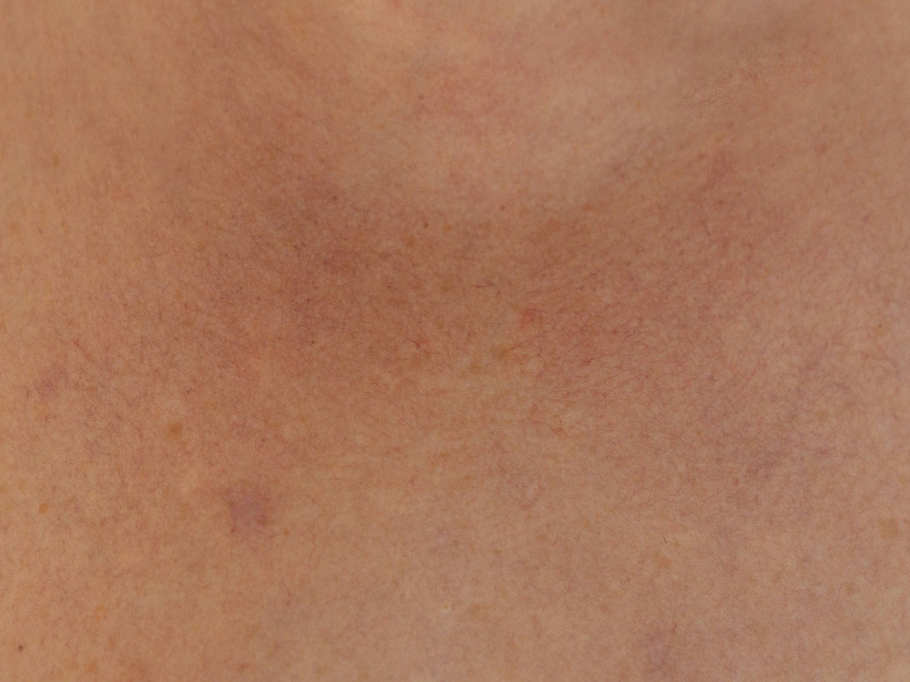
Rosacea is a common yet often misunderstood skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps, rosacea can be a source of discomfort and self-consciousness for those who experience it. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are key steps in managing this chronic condition effectively.
What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the face. It tends to occur in cycles, with periods of flare-ups followed by periods of remission. While anyone can develop rosacea, it is most commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals between the ages of 30 and 50. It’s more prevalent among women, although men can also be affected, often with more severe symptoms.
Rosacea is not just a cosmetic issue; it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. The condition can cause discomfort, pain, and emotional distress, especially when it interferes with daily activities and social interactions.
Common Symptoms of Rosacea
The symptoms of rosacea can vary widely from person to person, but the most common signs include:
- Facial Redness: Persistent redness, especially on the cheeks, nose, chin, or forehead, is a hallmark of rosacea. This redness often looks like a sunburn or blush that doesn’t go away.
- Visible Blood Vessels: Small blood vessels on the surface of the skin, known as telangiectasia, can become visible, contributing to the overall redness.
- Bumps and Pimples: Rosacea can cause acne-like breakouts, including small red bumps (papules) and pus-filled pimples (pustules). Unlike acne, these bumps don’t typically result in blackheads.
- Eye Irritation: Known as ocular rosacea, this type affects the eyes, leading to redness, dryness, itching, and a gritty sensation. In severe cases, it can cause vision problems.
- Thickened Skin: Over time, rosacea can cause the skin, particularly on the nose, to thicken and enlarge, a condition known as rhinophyma. This is more common in men than women.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Many people with rosacea report a burning, stinging, or itching sensation on their face, especially during flare-ups.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. Genetics play a role, as a family history of rosacea may increase the risk of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Additionally, an overactive immune response, particularly involving a protein called cathelicidin, might contribute to the inflammation seen in rosacea. Environmental factors such as sun exposure, heat, cold, wind, and humidity can also trigger or worsen symptoms. Diet and lifestyle choices, including the consumption of spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and stress, are common triggers for many individuals with rosacea. Finally, the presence of specific microorganisms, like the mite Demodex folliculorum and the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, has been linked to rosacea. However, their exact role in the condition still needs to be fully understood.
Managing and Treating Rosacea
While there is no cure for rosacea, various treatments can help manage and reduce symptoms. The right approach often depends on the severity of the condition and individual triggers.
- Topical Treatments: Medications like metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and redness. These are applied directly to the affected skin.
- Oral Medications: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline can be used to reduce inflammation. For those with acne-like symptoms, oral isotretinoin might be considered.
- Laser and Light Therapy: Laser treatments from Flora Aesthetics & Wellness can help reduce the appearance of visible blood vessels and redness. Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy is another option that targets both redness and visible blood vessels.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial in managing rosacea. Keeping a diary to track flare-ups and their potential causes can be helpful. Sun protection is also essential, as UV exposure can worsen symptoms.
- Skin Care: Using gentle, fragrance-free skin care products can help minimize irritation. It’s also important to moisturize regularly and avoid harsh exfoliants or scrubs.
- Eye Care: For those with ocular rosacea, eye drops, eyelid hygiene, and oral antibiotics may be recommended. Regular visits to an eye care specialist are important for managing symptoms.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with rosacea can take an emotional toll, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Many people with rosacea feel self-conscious about their appearance, leading to social anxiety or even depression. It’s important to address these feelings and seek support if needed. Speaking with a dermatologist about the best treatment options and connecting with others with rosacea can also be helpful.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex condition requiring a personalized treatment and management approach. While it can be challenging to live with, understanding the triggers, symptoms, and available treatments can empower those affected to take control of their condition. With the right care and lifestyle adjustments, many people with rosacea can effectively manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. If you suspect you have rosacea, consulting with a dermatologist is the first step toward finding relief and developing a management plan tailored to your needs.